

Sort an array in descending order based on the given expression.Īn object with fields for each gender found in the 'children' array. The children array sorted from highest age to lowest. Sort an array in ascending order based on the given expression. The children array sorted from lowest age to highest. Note that we do not actually use the result of the path here. The value of the 'pipe_param' pipeline parameter. The 'value' variable is set to the result of the query. The first child whose age is greater than 18.Įvaluate an expression on the result of the path. $.children.map()Īn array of all the children objects that has been remapped so that there is only a single 'name' field instead of 'fname' and 'lname'. The 'value' variable will be set to the value of the current element. Iterate over the elements of an array, execute the given expression for each element, and return an array with the results. So, rather than require an extra Snap to extract the address object from a list, we have extended the standard JSONPath syntax with some method calls that can be used to manipulate the results of a query.Īn array of all the 'age' fields from the objects in the 'children' array. $.addresses), but the result is still in a list. home, work), you could use a filter to select the home address (i.e. When using JSONPath to query a document, the basic syntax can cover the majority of use-cases, however, there are often times when you wish to process the results of a query. For example, if an array contained a list of addresses (e.g. If any part of the path is missing, then the default value is returned. Sets a default value for JSONPath. If a specified path exists, it's value is returned. When the book author is not found, the author is listed as Anonymous. Select the array element or object field as specified by the enclosed expression. The field from the 'parent' object that is specified by the 'name' pipeline parameter. In the expression, the 'value' variable refers to the array element or object value and the 'key' variable refers to the field name in the object. Selects all elements in an array or an object that match the given expression. Only those elements in the 'children' array where the 'age' field is greater than 18. Selects the array elements or object fields with the given indexes or names, respectively. The fields of the 'parent' object named 'child1' and 'child2'.

If the 'start' or 'end' values fall outside of the bounds of the array, they will automatically be adjusted to the nearest bounds and not trigger an error.Įvery other element in the 'children' array.Īll elements of the 'children' array in reverse order. The 'step' value specifies how many elements the operator moves through at a time. If no end is given, then the end of the list is used. The 'end' value specifies the exclusive end of the slice. If not specified, then zero is used for the start. The 'start' value specifies the starting index for the slice.
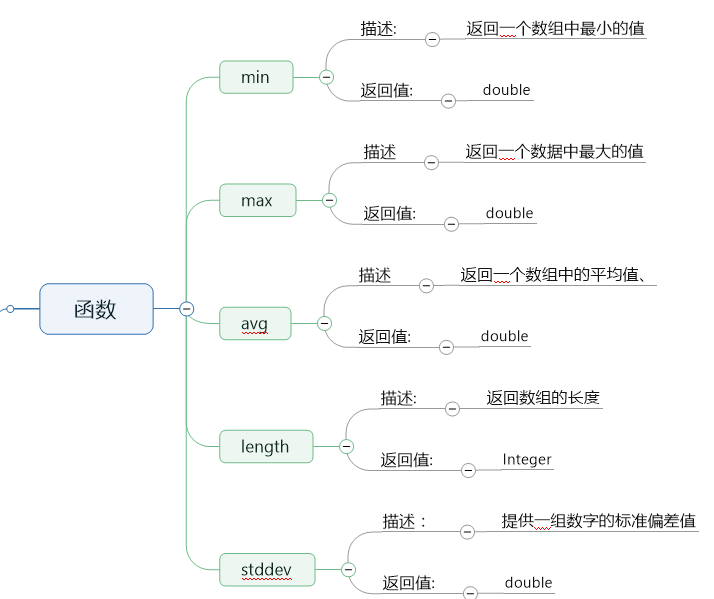
Traverses the entire document searching for the fields and elements that match the rest of the path.Īll but the first element of the 'children' array. Selects all elements in an array or an object.Īll of 'child' fields found in the document. The 'age' values from the elements of the 'children' array. The second element of the ' child' array. This operator can used to select a field that may contain special characters that need to be quoted. The 'child with spaces' field from the 'parent' object.Ĭhild operator or array index. This operator is used to select a field in a parent object. The 'child' field from the 'parent' object.Ĭhild operator. The basic syntax supported by the Snaps follows the original JSONPath specification. The following is a summary of the syntax. Mapper (Data) - The Mapper (Data) Snap evaluates an expression and writes the result to the destinations given by the target JSONPath. Be aware that the expression language syntax and JSONPath syntax are not compatible. Simple syntax like "$.name" is valid in both, but anything non-trivial will likely not work. Structure - The Structure Snap allows you to reshape a document, moving values, deleting fields, and so on.
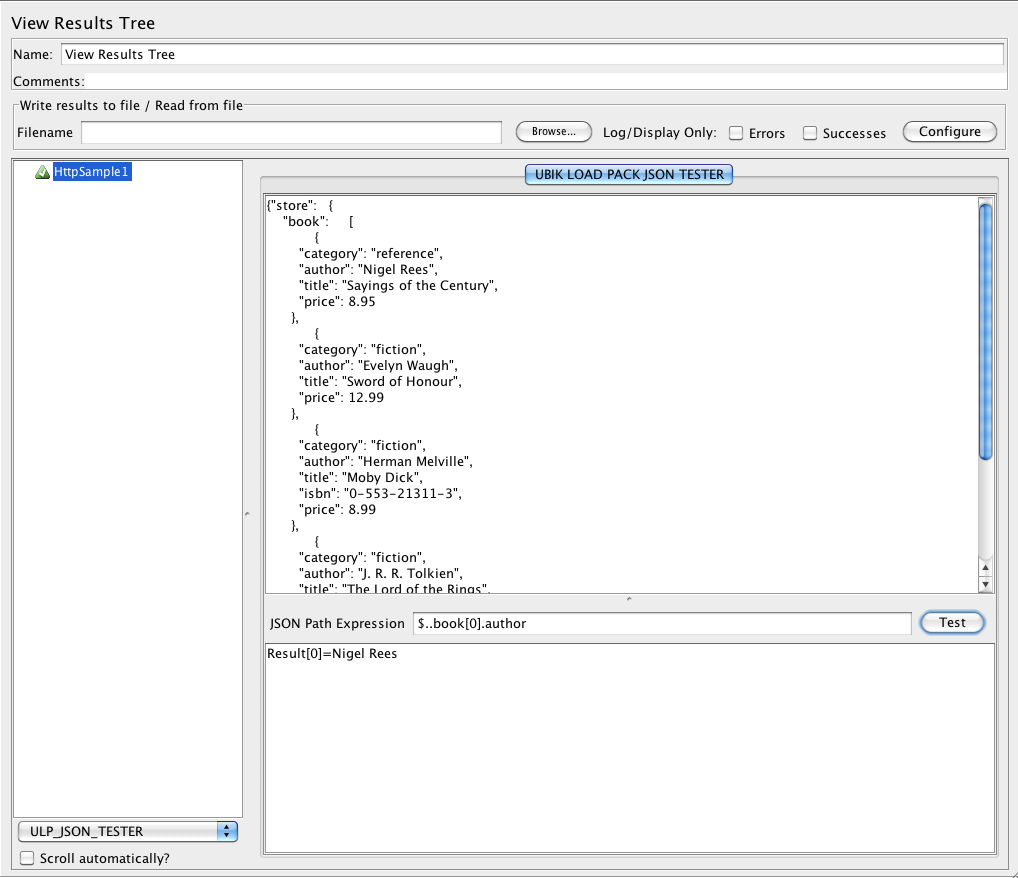
A JSONPath expression lets you specify the parts of a JSON document that are to be operated on by a Snap. For example, to reference the "name" field at the root of a document, you can use the path "$.name". More complex paths are also possible that will let you walk an entire document looking for a particular field, filter objects based on their value, and so on. If you are familiar with XPath for XML documents, than JSONPath is a similar concept for JSON documents.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
